Additive Manufacturing
Metal additive manufacturing is a new technology, also known as 3D printing, that selectively melts the starting raw material for each layer and repeats for multiple layers to build a three-dimensional object.
There are seven types of methods, not limited to metals, defined as ISO 17296-2: 2015 AM Part 2 by the ISO / TC 261 Additive manufacturing Technical Committee expert committee 261 under the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
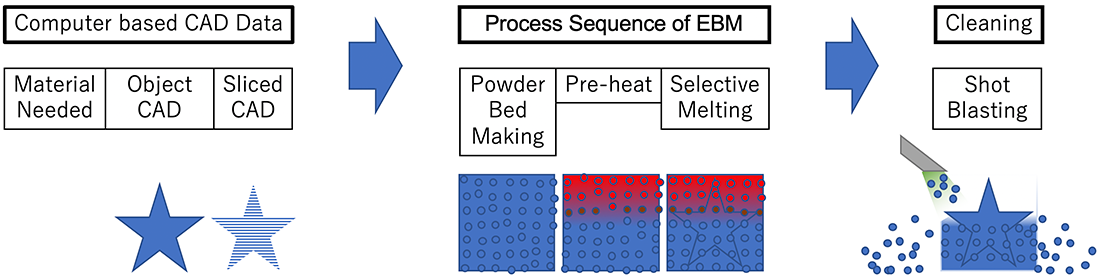
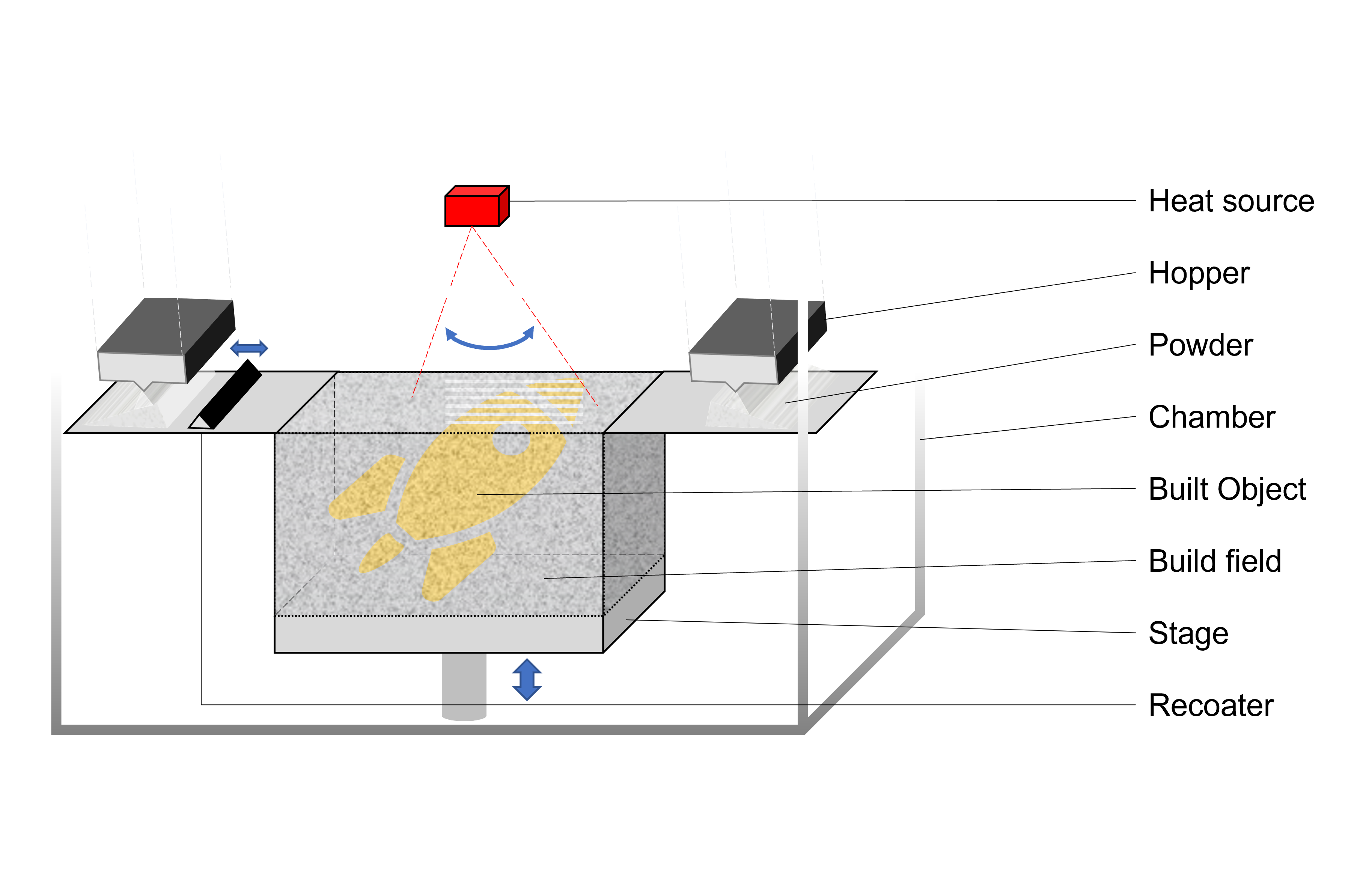
1. Powder Bed Fusion
This method builds object by repeating powder bed forming and heat source scanning.
[Powder Bed Making] The powder bed is formed by laying powder from powder hopper onto the stage with a recoater. [Melting and Solidifying] The heat source of a laser or an electron beam selectively scans the surface of the powder bed to melt and solidify instantaneously and locally. The stage is lowered by one layer, and the powder bed is newly formed and scanned to build the desired object.
This method utilizes fine powder (10-100 μm) so that a precise build is expected. In addition, a real time feeding back of melt-solidification simulation with computer-based 3D modeling to the real build will be expected to control accuracy and structure of the desired object.
PBF-LB/M、PBF-E/M、EBM、DMLS、SLS、SLM、MJF
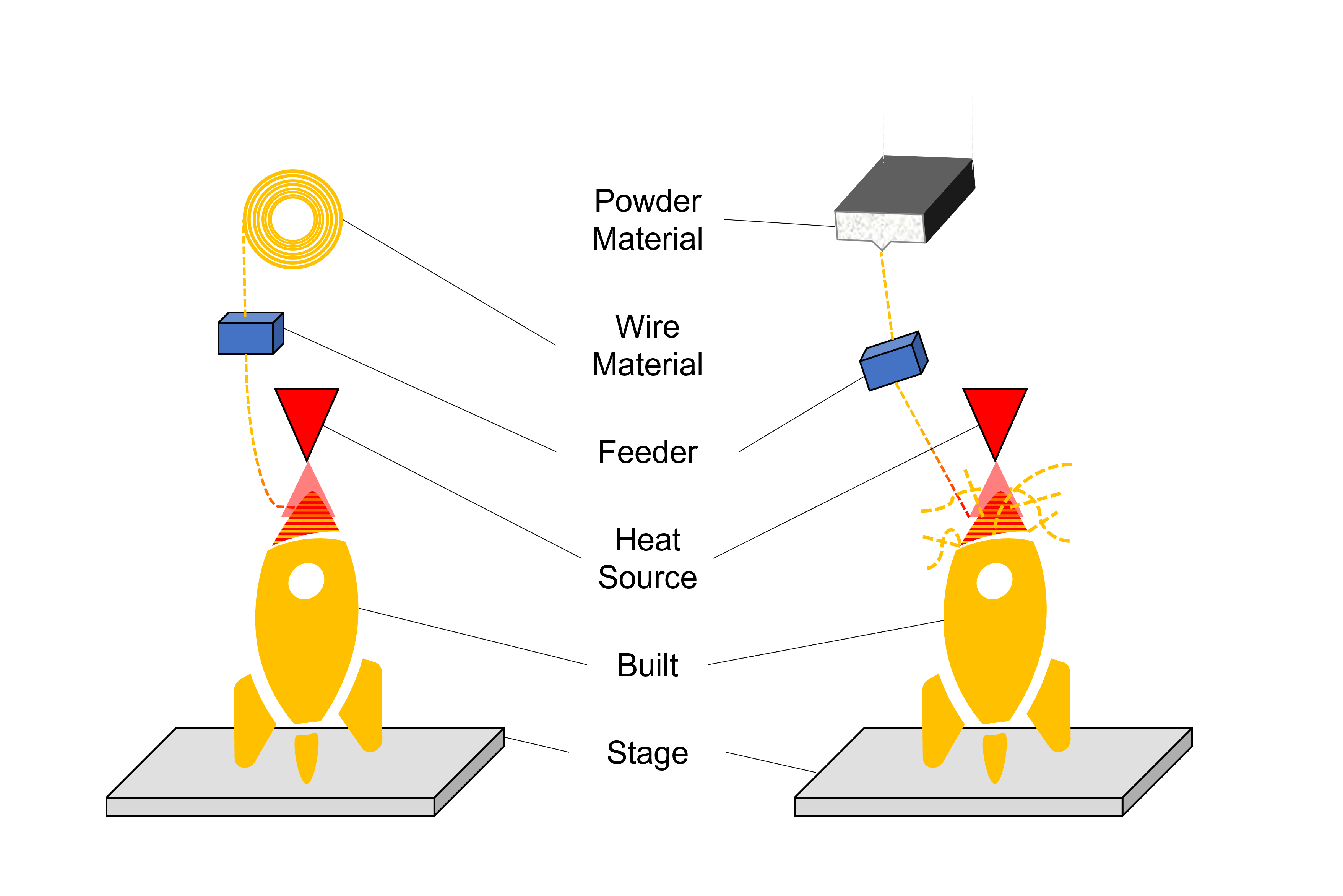
2. Directed Energy Deposition
This method builds object through deposition of raw material to melted zone.
[Melting] The relevant part is melted by a heat source, and [Deposition] the raw material is deposited in the molten pool from the feeder to build the desired object.
It is the same method as laser cladding or buildup welding. This method varies depending on the shape of supply material (powder or wire) and the heat source (laser beam, electron beam or arc). This method utilizes coarse powder (50-150 μm) or thick wire (φ1-3 mm) so that a rough build is expected. Currently, this method is the most suitable for high-speed building of large object in the atmosphere or under protective shields.
DED、WAAM、LMD、EBAM、WLAM、LENS、LDW
3. Material Extrusion
This method builds object by drawing of heated thermoplastic filament with raw material through a nozzle to form shape as the desired. Thereafter, a heat treatment is required for sintering and degreasing.
[Forming] A thermoplastic filament containing the raw material is heated from the feeder and extruded onto the stage to form shape as the desired. [Heat Treatment] Thereafter, the object requires heat treatment in a furnace for degreasing.
This method is currently the cheapest among metal 3D printing. Note that volume changes significantly before and after heat treatment, and it is necessary to consider the rate of change in advance.
FDM、FFF
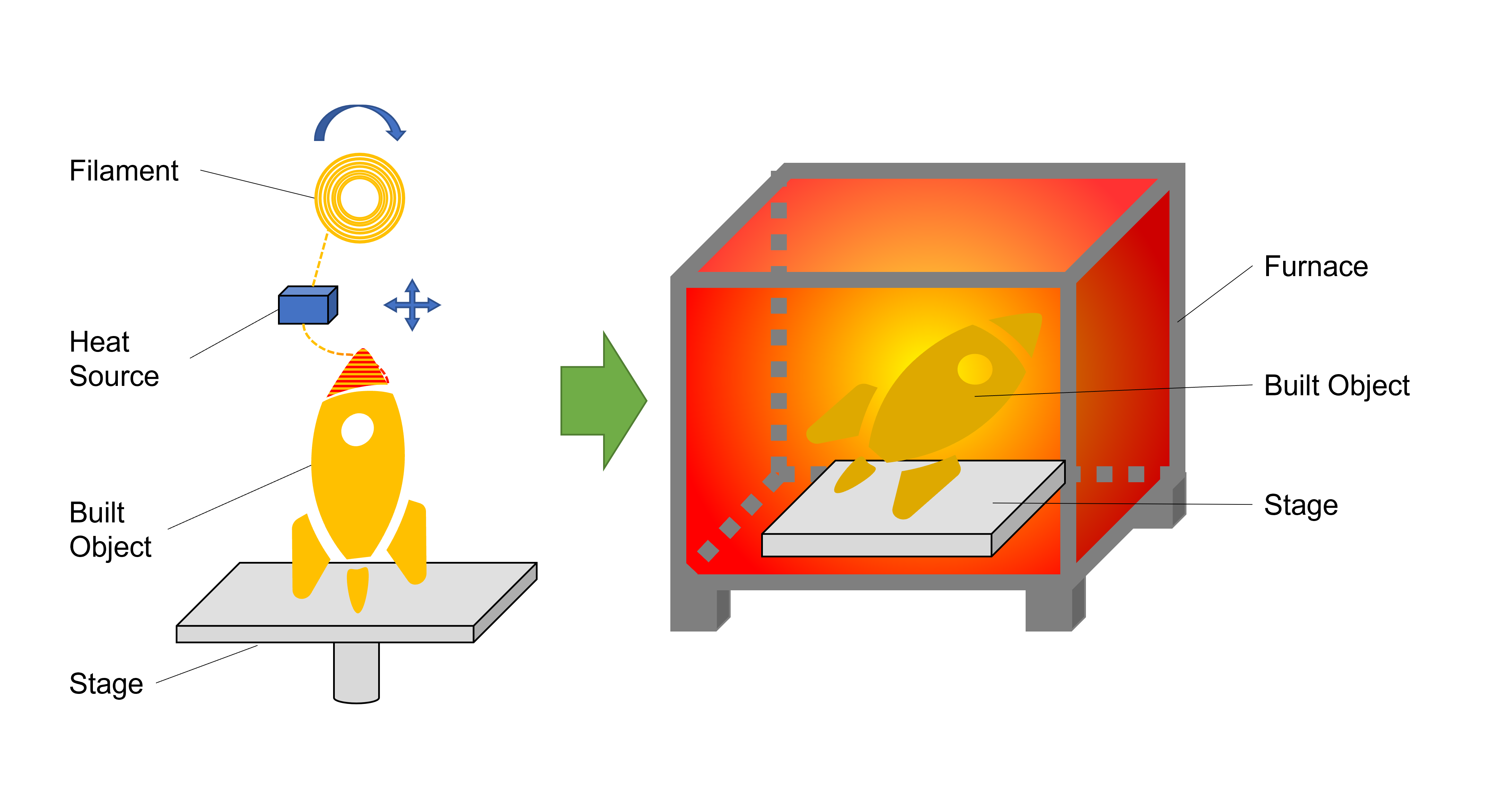
4. Binder Jetting
This method builds object by repeating powder bed forming and binder dipping. Thereafter, a heat treatment is required for sintering and degreasing.
[Powder Bed Making] The powder bed is formed by laying powder from powder hopper onto the stage with a recoater. [Gluing] The print head selectively dips liquid binder on the surface of the powder bed as “glue”. The stage is lowered by one layer, and the powder bed is newly formed with the binder dipping. [Heat Treatment] At last, the object requires heat treatment in a furnace for degreasing and sintering.
This method is currently the cheapest for mass-production. Many companies are embracing this approach, from HP’s large devices to ExOne’s small devices. Compared with PBF, the residual stress of the built object can be prevented due to no heat involved during the process, but the mechanical properties are inferior due to due to incomplete melting.
BJ
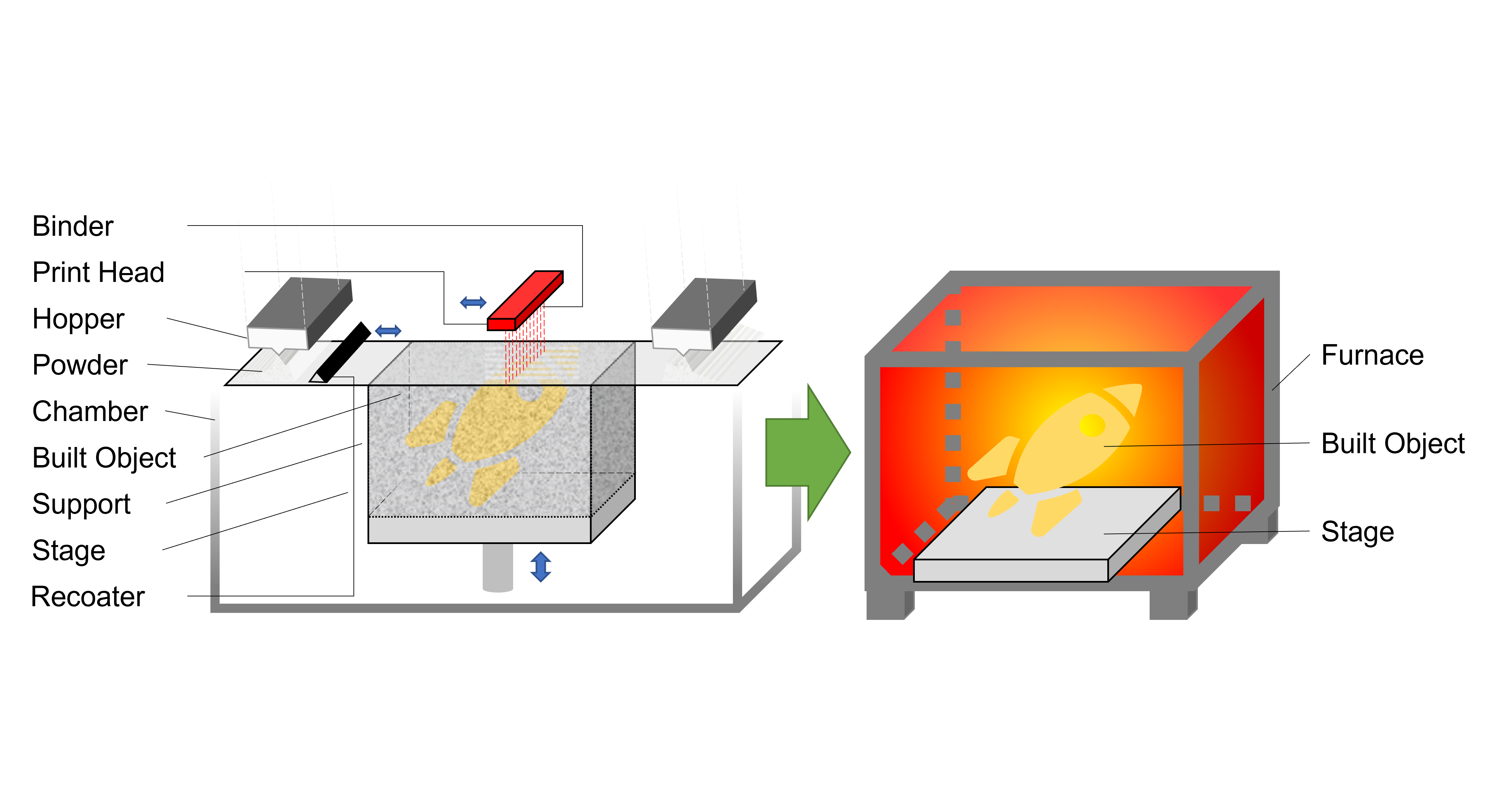
5. Material Jetting
This method builds object by dropping liquid droplet with raw material to form shape as the desired. Thereafter, a heat treatment is required for sintering.
[Forming] Liquid droplet containing the raw material is dropped from the print head on the stage, [Heat Treatment] and each layer is sintered by heat treatment.
As of 2021, Xjet is the only manufacturer shows the most promise for metal material jetting, which evaporating droplets containing metal nanoparticles (NanoParticle Jetting, NPJ). Others are such as resin and lost wax casting.
The problems are long-time building and expensive cost.
MJ, NPJ, DOD
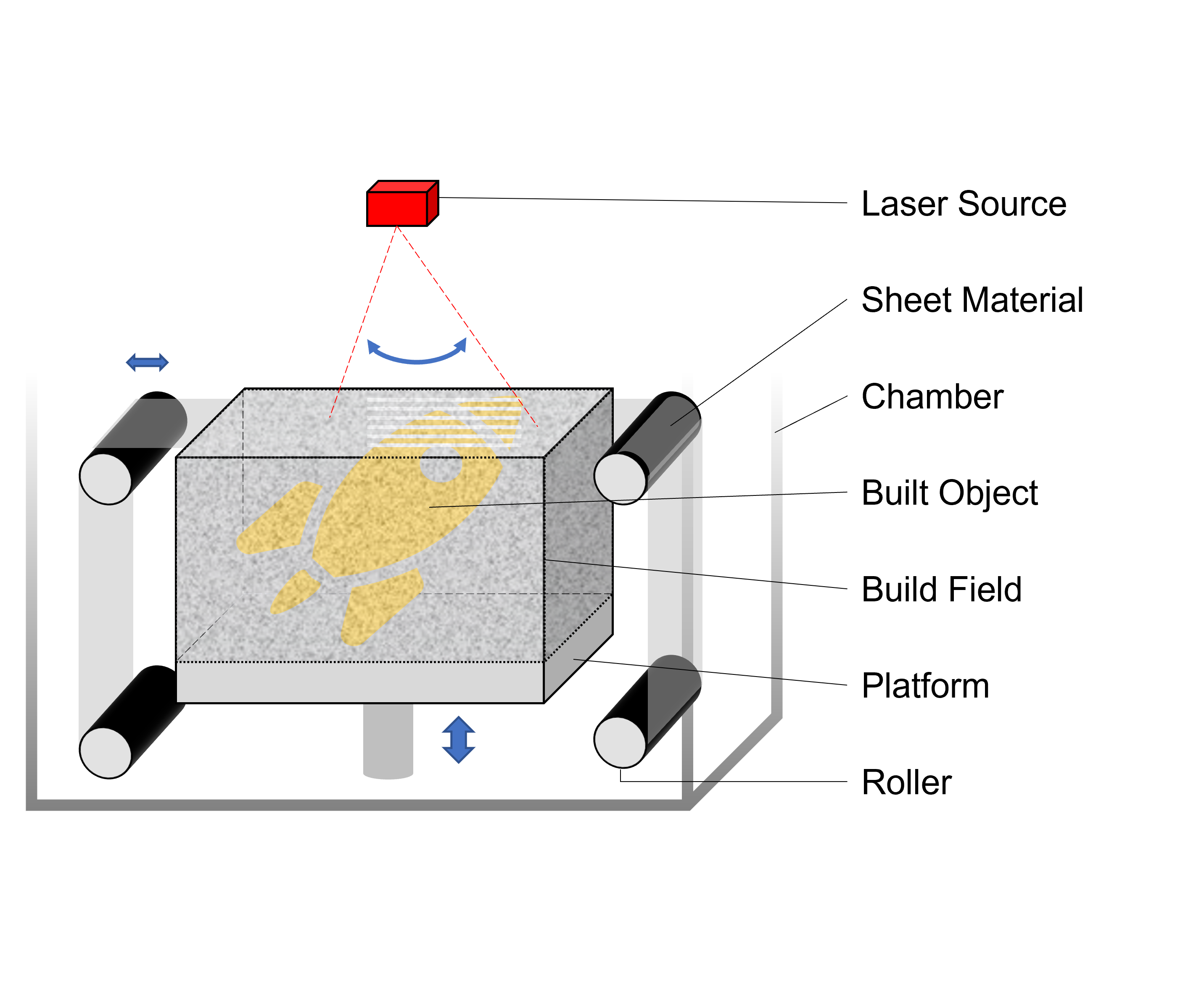
6. Sheet Lamination
This method builds object by cutting out and joining metal sheet materials.
[Forming] While the sheet material is welded and bonded layer by layer with a laser or ultrasonic source, [Peeling] the relevant part is hollowed out with a laser or a cutter to form a model.
As of 2021, not only metals but also paper, polymers, resins and ceramics are available. However, the number of metal sheet materials that can be produced is limited, and the total number is still small.
SLCOM, UAM, LOM, SL
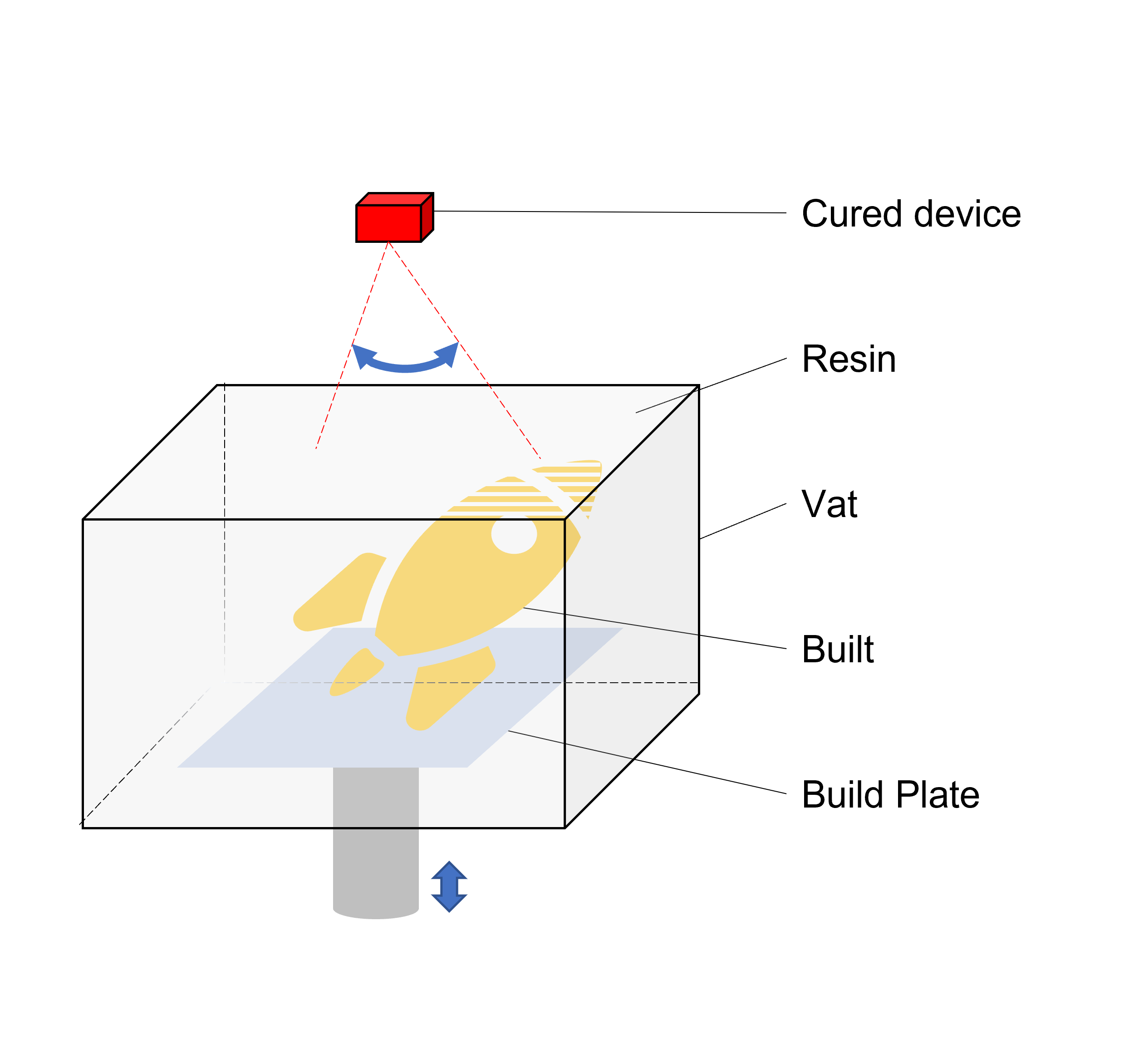
7. Vat Photopolymerization
This method builds object by selectively curing the resin with an ultraviolet (UV) light.
[Curing] The UV light is used to selectively cure or harden a vat of liquid photopolymer resin layer by layer. After completion, the vat is drained of resin and the object removed.
VAT、SLA、DLP、CDLP